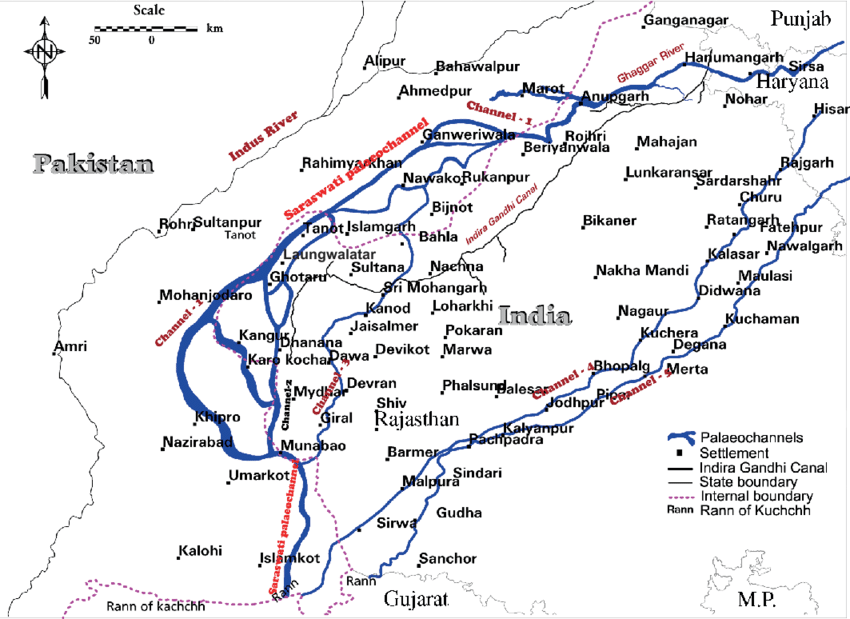
The 7 Rivers Civilization, more commonly known as the Indus Valley Civilization, stands as one of the oldest and most enigmatic cultures in human history. Emerging around 3500 BCE, it flourished in the fertile plains of the Indus and Sarasvatî rivers, reaching its zenith before gradually declining around 1900 BCE.
This civilization is renowned for its advanced urban planning, groundbreaking architectural innovations, and remarkable engineering achievements, making it a cornerstone of ancient human development.
Urban Wonders: The Heart of the Indus Valley
The cities of the 7 Rivers Civilization, such as Harappa and Mohenjo-Daro, reveal an extraordinary mastery of urban design. These metropolises featured:
- Grid-organized streets: A testament to meticulous planning.
- Sophisticated drainage systems: Preventing floods and ensuring hygiene.
- Uniform brick constructions: Showcasing standardization in architecture.
These innovations reflect a society deeply invested in functionality and sustainability, long before modern urban concepts.
A Thriving Economy Rooted in Agriculture and Trade
The economy of the Indus Civilization revolved around a robust agricultural base, with crops like:
- Wheat and barley, staples of their diet.
- Cotton, which they were among the first to cultivate.
Trade was equally vital, with long-distance exchanges connecting them to Mesopotamia, where goods such as beads, textiles, and precious metals were bartered. These interactions not only enriched their economy but also facilitated the exchange of ideas and cultural practices.
Spiritual Insights: The Rig Veda and Beyond
A unique aspect of this civilization is its connection to the Rig Veda, one of the oldest known religious texts in the world. This collection of hymns and philosophical reflections provides a glimpse into the:
- Rituals and spiritual practices of the era.
- Philosophical depth that laid the foundation for Indian spirituality.
The Rig Veda continues to influence millions globally, symbolizing a timeless bridge between past and present.
The Decline: A Civilization’s Challenges
Despite its advancements, the Indus Civilization faced environmental and geological hurdles. Climatic shifts and two major earthquakes played a significant role in its decline. However, parts of the civilization, especially in Gujarat, endured for several centuries beyond its supposed fall.
The Legacy of the 7 Rivers Civilization
The ingenuity, culture, and contributions of this civilization remain a source of inspiration. From urban planning principles to spiritual legacies, its influence is woven into the fabric of modern societies, particularly in the Indian subcontinent.
Key Takeaways
The 7 Rivers Civilization stands as a testament to humanity’s potential for innovation, resilience, and cultural richness. Its legacy, though ancient, continues to echo in contemporary thought, art, and spirituality.